A. Definition of Polyphony
1. Origin of the Term
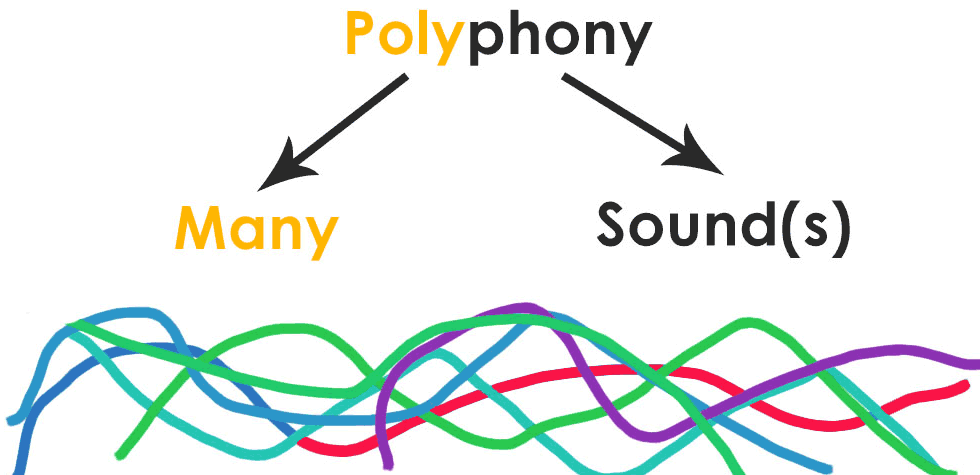
The term polyphony comes from the Greek words “poly” (many) and “phony” (sound), which together mean “many sounds.” It was initially used to describe a type of music characterized by multiple independent voices or melodies.
2. Meaning in Music and Digital Piano Context
In the context of digital pianos, polyphony refers to the maximum number of notes that can be played simultaneously without any of them being cut off or dropped. It is a crucial factor in determining the expressiveness and performance capabilities of a digital piano.
B. Importance of Polyphony in Digital Pianos
1. Role in Music Composition and Performance
Polyphony plays a significant role in music composition and performance, as it allows musicians to create complex harmonies, layer multiple voices, and achieve intricate counterpoints. A digital piano with a higher polyphony count enables the player to perform more complicated pieces without limitations.
2. Enhancing the Expressiveness of the Instrument
Higher polyphony allows for greater expressiveness, as it enables the pianist to sustain notes, use the sustain pedal, and create rich, layered sounds. For example, a digital piano with 128-note polyphony can produce more expressive and nuanced performances than one with only 64-note polyphony.
C. The Evolution of Polyphony in Digital Pianos

1. Technological Advancements in Digital Piano Design
Over time, technological advancements have allowed for significant improvements in digital piano design, resulting in higher polyphony counts. Early digital pianos had polyphony counts as low as 16 notes, while today’s models can reach 256 notes or more.
2. The Increasing Demand for More Expressive Instruments
As musicians and composers continue to push the boundaries of their craft, there is a growing demand for digital pianos that offer greater expressiveness and performance capabilities. As a result, manufacturers like Casio continue to innovate and develop digital pianos with higher polyphony counts to meet these needs.
A. Understanding Polyphony in Digital Pianos
1. The Concept of Note Generation and Decay
When a digital piano key is pressed, it generates a note. As more keys are pressed, more notes are created. Each note has a natural decay, fading out over time. Polyphony determines the maximum number of notes that can exist simultaneously without affecting the quality of the sound.
2. Maximum Polyphony and Its Implications
The maximum polyphony of a digital piano is crucial for creating rich, layered sounds without losing any notes. When the polyphony limit is reached, the piano will begin to drop the oldest notes, affecting the overall sound quality. Higher polyphony counts provide more flexibility for complex performances and musical expression.
B. Factors Affecting Polyphony in Digital Pianos
Sound Engine Technology
a. Sample-Based Synthesis
Sample-based synthesis utilizes pre-recorded audio samples of real acoustic instruments, such as grand pianos. While this technology can produce realistic and expressive sounds, it requires a significant amount of memory, which can limit polyphony.
b. Physical Modeling Synthesis
Physical modeling synthesis recreates the sound of an instrument by simulating its physical properties. This method can produce highly realistic sounds while using less memory, allowing for higher polyphony counts. However, it may require more processing power, as seen in the Casio CDP-S360.
c. Virtual Acoustic Synthesis
Virtual Acoustic synthesis combines aspects of both sample-based and physical modeling techniques, resulting in a balance between realism and performance. Some Roland digital pianos use this technology to deliver high polyphony counts and expressive sound.
d. Impact on Polyphony and Performance
The amount of memory and processing power in a digital piano directly impacts polyphony and overall performance. More memory allows for higher polyphony counts and more complex sound generation, while faster processors can handle the computational demands of advanced synthesis techniques.
C. Polyphony in Different Types of Digital Pianos

1. Entry-Level Digital Pianos
a. Typical Polyphony Range
Entry-level digital pianos usually have polyphony counts between 32 and 64 notes, making them suitable for beginners and casual players who need basic functionality at an affordable price. However, this limited polyphony can restrict expressive capabilities and might not be sufficient for more advanced pieces.
b. Limitations in Expressive Capabilities
With lower polyphony counts, entry-level digital pianos may struggle to deliver the expressive range required for complex compositions. For example, using the sustain pedal or playing fast passages with multiple voices can cause notes to drop, affecting the overall sound quality.
2. Intermediate Digital Pianos
a. Increased Polyphony Range
Intermediate digital pianos offer polyphony counts between 64 and 128 notes, providing more flexibility for a broader range of music styles. These pianos are suitable for intermediate players and aspiring professionals who require better performance capabilities and expressiveness.
b. Enhanced Expressiveness and Performance
With higher polyphony counts, intermediate digital pianos allow for more complex compositions and better overall sound quality. For example, pianos like the Casio CDP-S360 can handle more intricate pieces without note-dropping, providing a more satisfying playing experience.
3. High-End Digital Pianos
a. Maximum Polyphony Range
High-end digital pianos typically offer polyphony counts of 128 notes and above, with some models reaching 256 notes or more. These pianos cater to professional musicians and advanced players who demand the highest levels of performance and expressiveness.
b. Advanced Features for Professional Musicians
In addition to high polyphony counts, high-end digital pianos often include advanced features such as realistic touch response, high-quality samples, and customizable settings. Examples include the Yamaha P515 and the Roland FP-60X.
D. The Role of Polyphony in Various Music Genres and Playing Styles
1. Classical Music
a. Complex Compositions and Polyphony Requirements
Classical music often features intricate compositions with multiple voices, requiring a high polyphony count to maintain note clarity and prevent note dropping. Digital pianos with higher polyphony counts are better suited for performing classical pieces.
b. Examples of Famous Polyphonic Pieces
Famous polyphonic pieces that require high polyphony counts include J.S. Bach’s fugues, such as the “Well-Tempered Clavier,” and Beethoven’s piano sonatas, like the “Moonlight Sonata.”
2. Jazz and Improvisation
a. Polyphony in Layered Textures and Chordal Harmony
Jazz music often involves complex chordal harmony and layered textures, requiring digital pianos with higher polyphony counts to achieve the desired expressiveness. Additionally, jazz improvisation can demand rapid note changes and the use of multiple voices simultaneously.
b. Expressive Potential in Jazz Performances
A digital piano with high polyphony count allows jazz musicians to explore their creative potential and express themselves more freely during performances.
3. Pop and Contemporary Music
a. Simpler Polyphony Requirements
Pop and contemporary music generally require less polyphony than classical or jazz music, as they often feature simpler chord progressions and melodies. As a result, digital pianos with lower polyphony counts may be sufficient for most pop and contemporary music performances.
b. Creative Potential in Sound Design and Composition
However, some pop and contemporary musicians may still benefit from higher polyphony counts for creative sound design and composition, especially when using DAW integration and MIDI controllers like the Akai MPK261.
E. Comparing Polyphony in Digital Pianos and Acoustic Pianos
1. The Inherent Polyphony of Acoustic Pianos
a. Natural Resonance and Harmonics
Acoustic pianos have an inherent polyphony due to their design, allowing for natural resonance and harmonics. However, the number of simultaneous notes is limited by the number of keys (88 on a standard piano) and the physical constraints of the instrument.
b. Limitations in Comparison to Digital Pianos
While acoustic pianos provide a natural, expressive sound, they may not offer the same level of flexibility and customization as digital pianos. Additionally, acoustic pianos may require more frequent maintenance and tuning, making them less practical for some musicians.
2. Advantages of Digital Piano Polyphony
a. Flexibility and Customization
Digital pianos provide several advantages over acoustic pianos, including the ability to adjust polyphony counts, sound settings, and even instrument voices. This flexibility allows musicians to tailor their instruments to their specific needs and preferences, making digital pianos a popular choice for various music genres and styles.
b. Integration with Modern Music Production Tools
Digital pianos also offer seamless integration with modern music production tools, such as DAWs and MIDI controllers. This integration allows musicians to experiment with sound design, create complex arrangements, and produce professional-quality recordings using their digital piano as a central component of their setup.
A. Recap of Polyphony’s Importance in Digital Pianos
1. Expressiveness and Performance Capabilities
Polyphony plays a critical role in the expressiveness and performance capabilities of digital pianos, allowing musicians to create intricate compositions, experiment with various playing styles, and achieve the desired sound quality. High polyphony counts ensure that notes are not dropped during complex passages, ensuring a more satisfying playing experience.
2. Adaptability to Various Music Genres and Styles
Digital pianos with higher polyphony counts can cater to a wider range of music genres and styles, from classical and jazz to pop and contemporary music. This adaptability makes digital pianos a popular choice for musicians of all levels and preferences.
B. The Future of Polyphony in Digital Pianos
1. Technological Advancements and Potential Improvements
As technology continues to advance, digital pianos are likely to see further improvements in polyphony capabilities, sound quality, and overall performance. Innovative sound engine technologies and increased processing power will allow for even more expressive and realistic digital piano experiences, such as those found in the Roland FP-30X and the Yamaha P125.
2. Integration with Other Instruments and Music Production Tools
The future of polyphony in digital pianos may also involve greater integration with other instruments and music production tools, enhancing their versatility and creative potential. This integration will enable musicians to collaborate more efficiently, experiment with new sounds, and produce professional-quality recordings using their digital pianos as a central component of their setup.
C. Final Thoughts
1. The Role of Polyphony in the Overall Digital Piano Experience
Polyphony plays a vital role in the overall digital piano experience, influencing the instrument’s expressiveness, performance capabilities, and suitability for different music genres and styles. Understanding the importance of polyphony can help musicians make informed decisions when selecting a digital piano that meets their needs and preferences.
2. The Importance of Selecting the Right Instrument Based on Individual Needs and Preferences
Ultimately, the choice of a digital piano should be based on the individual needs and preferences of the musician, taking into consideration factors such as polyphony, sound quality, and available features. By selecting the right instrument, musicians can fully explore their creative potential and enjoy a satisfying, expressive playing experience.
Digital Piano Maintenance Tips are essential to keep your digital piano performing at its best, ensuring that the polyphony and other features continue to provide a top-notch experience for years to come.